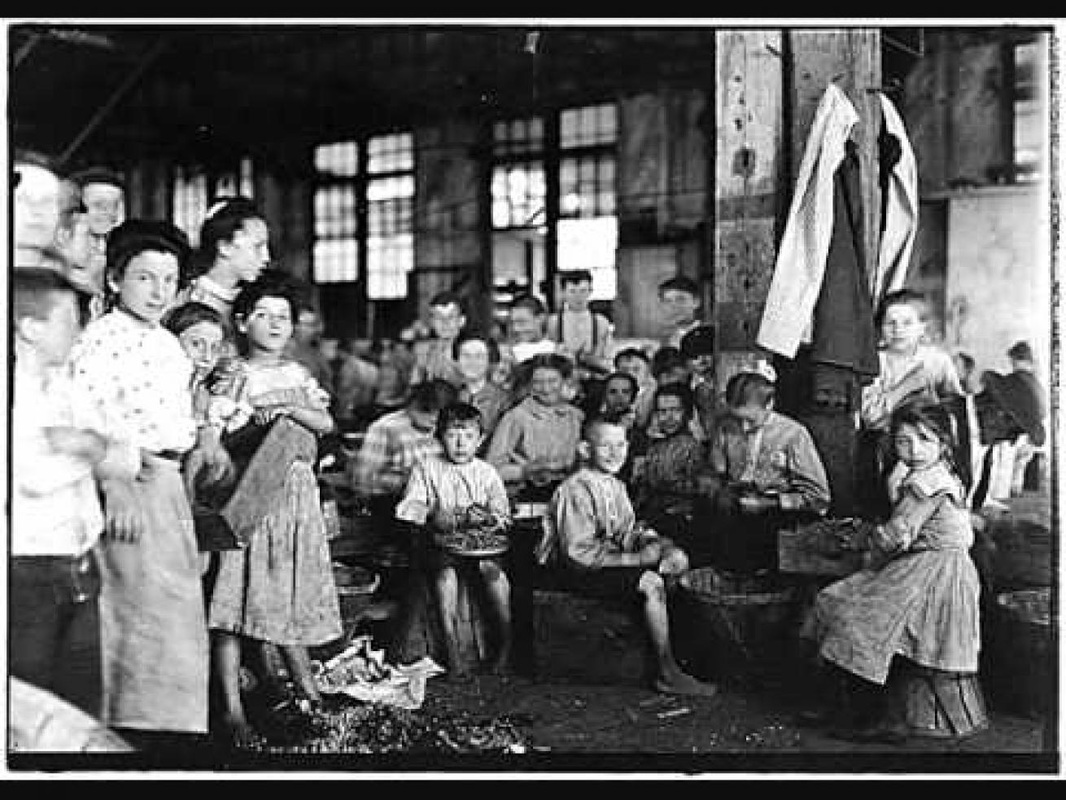

Child Labor The Second Industrial Revolution 1870 1914 Disadvantages Child labour was always used in agriculture and cottage industries, but with the arrival of the industrial revolution, children were systematically used in mines and factories, often doing work specific to them for low pay and in poor conditions. While it was more prominent in some areas than others, nearly 20% of the workforce during the industrial revolution consisted of children and teenagers under 16 years old. in this post, we’ll examine why there was such a boom in child labor during this time.

Child Labor During The Industrial Revolution 1 Min Read Men who had been child labourers were often unable to raise their own children without condemning them to child labour as well. this deleterious cycle not only impacted the health of current generations, but also future generations. Child labor was especially common in the late 18th century, during the early years of the industrial revolution. at the time, industrial cities and towns grew dramatically due to the migration of farmers and their families who were looking for work in the newly developed factories and mines. The use of child workers was a major problem during the industrial revolution, as it often led to poor health and even death for the children involved. many of them worked long hours in dangerous and unhealthy conditions, which took a toll on their physical and mental health. This article examines the historical debate about child labor in britain, britain’s political response to problems with child labor, quantitative evidence about child labor during the 1800s, and economic explanations of the practice of child labor.
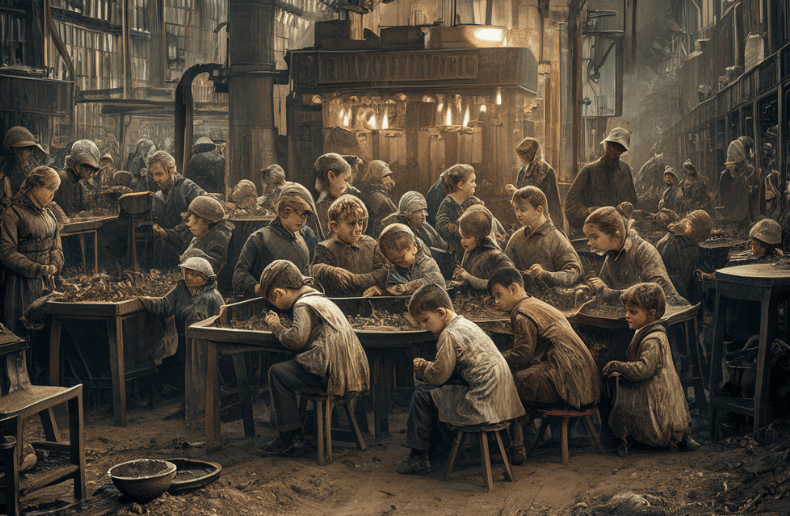
Industrial Revolution Research The use of child workers was a major problem during the industrial revolution, as it often led to poor health and even death for the children involved. many of them worked long hours in dangerous and unhealthy conditions, which took a toll on their physical and mental health. This article examines the historical debate about child labor in britain, britain’s political response to problems with child labor, quantitative evidence about child labor during the 1800s, and economic explanations of the practice of child labor. Children could typically work for 14 hours a day in factories, often with few or no breaks. children were also paid only a fraction of what an adult would get, and sometimes factory owners would get away with paying them nothing. Children were not treated well as they were overworked, and underpaid. children as young as six years old during the industrial revolution worked hard hours for little or no pay. children sometimes worked up to 16 hours a day, with a one hour total break. Child labor, or the use of children as workers, servants and apprentices, has been practiced throughout most of human history, but reached its zenith during the industrial revolution. Child labor became the labor of choice for manufacturing in the early phases of the industrial revolution because children were paid much less while being as productive as adults and were more vulnerable. their smaller size was also perceived as an advantage.
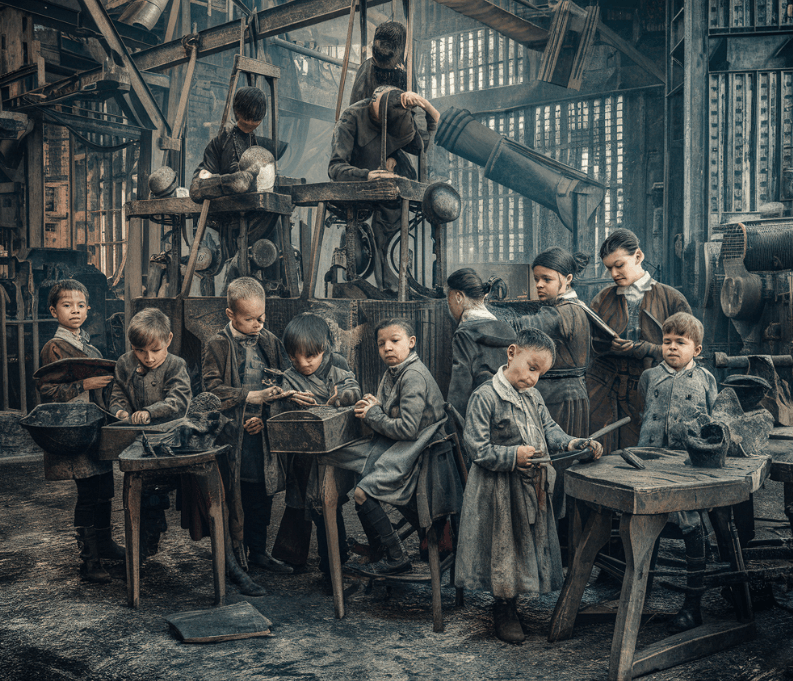
Industrial Revolution Research Children could typically work for 14 hours a day in factories, often with few or no breaks. children were also paid only a fraction of what an adult would get, and sometimes factory owners would get away with paying them nothing. Children were not treated well as they were overworked, and underpaid. children as young as six years old during the industrial revolution worked hard hours for little or no pay. children sometimes worked up to 16 hours a day, with a one hour total break. Child labor, or the use of children as workers, servants and apprentices, has been practiced throughout most of human history, but reached its zenith during the industrial revolution. Child labor became the labor of choice for manufacturing in the early phases of the industrial revolution because children were paid much less while being as productive as adults and were more vulnerable. their smaller size was also perceived as an advantage.
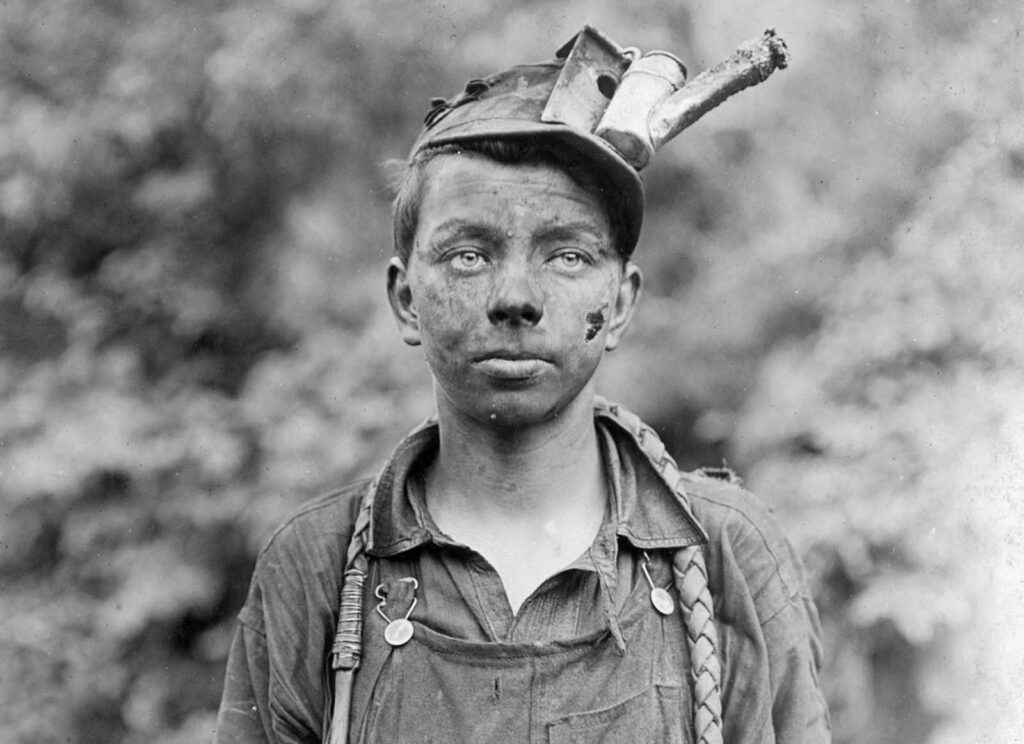

What Was Child Labor Like During The Industrial Revolution Child labor, or the use of children as workers, servants and apprentices, has been practiced throughout most of human history, but reached its zenith during the industrial revolution. Child labor became the labor of choice for manufacturing in the early phases of the industrial revolution because children were paid much less while being as productive as adults and were more vulnerable. their smaller size was also perceived as an advantage.
Comments are closed.